CoST – The Infrastructure Transparency Initiative created the Infrastructure Transparency Index (ITI) because we know efficient and effective delivery of public infrastructure is paramount for economic growth and social development.
Infrastructure projects are frequently susceptible to inefficiencies, mismanagement, and corruption, undermining public trust and hindering optimal outcomes. The ITI is a rigorous and practical methodology for measuring and enhancing transparency within infrastructure projects, fostering improved governance and project performance. Unlike many traditional transparency indexes that primarily focus on the availability of information, the ITI distinguishes itself by evaluating the entire ecosystem of transparency. It assesses the enabling legal and regulatory environment, the capacities of institutions to implement transparent practices, and the crucial element of citizen participation. These are factors that are demonstrably essential for translating transparency into tangible improvements in infrastructure project outcomes.
A Structured Approach to Transparency Measurement
The ITI is not merely a conceptual framework; it is a concrete and actionable tool that members can use to measure, monitor and demonstrate their infrastructure transparency, It has 4 main dimensions:
- Enabling Environment: This dimension examines the foundational legal and regulatory frameworks that underpin transparency in infrastructure projects. It assesses the existence and efficacy of laws, regulations, and digital tools that facilitate access to information and promotes open governance. Key considerations include the robustness of public information access laws, transparency standards specific to infrastructure, and the utilisation of national digital platforms for information dissemination.
- Capacities and Processes: This dimension evaluates the extent to which public institutions possess the necessary organizational capabilities, procedures, and technological infrastructure to effectively manage and share project information. It examines factors such as institutional knowledge of transparency standards, digital capabilities for information management, and established protocols for data disclosure.
- Citizen Participation: This dimension assesses the formal mechanisms and opportunities established by governments to facilitate meaningful citizen participation in infrastructure projects. It considers the accessibility of information for citizens, the avenues for public consultation, and the responsiveness of government to citizen feedback.
- Information Disclosure: This dimension rigorously evaluates the volume and quality of project information proactively published by procuring entities, adhering to international standards for planning, procurement, and execution. It assesses the comprehensiveness, accessibility, and timeliness of publicly available data, ranging from project identification and preparation to contract implementation and environmental impact assessments.
ITI Implementation: Tangible Impact and Global Relevance
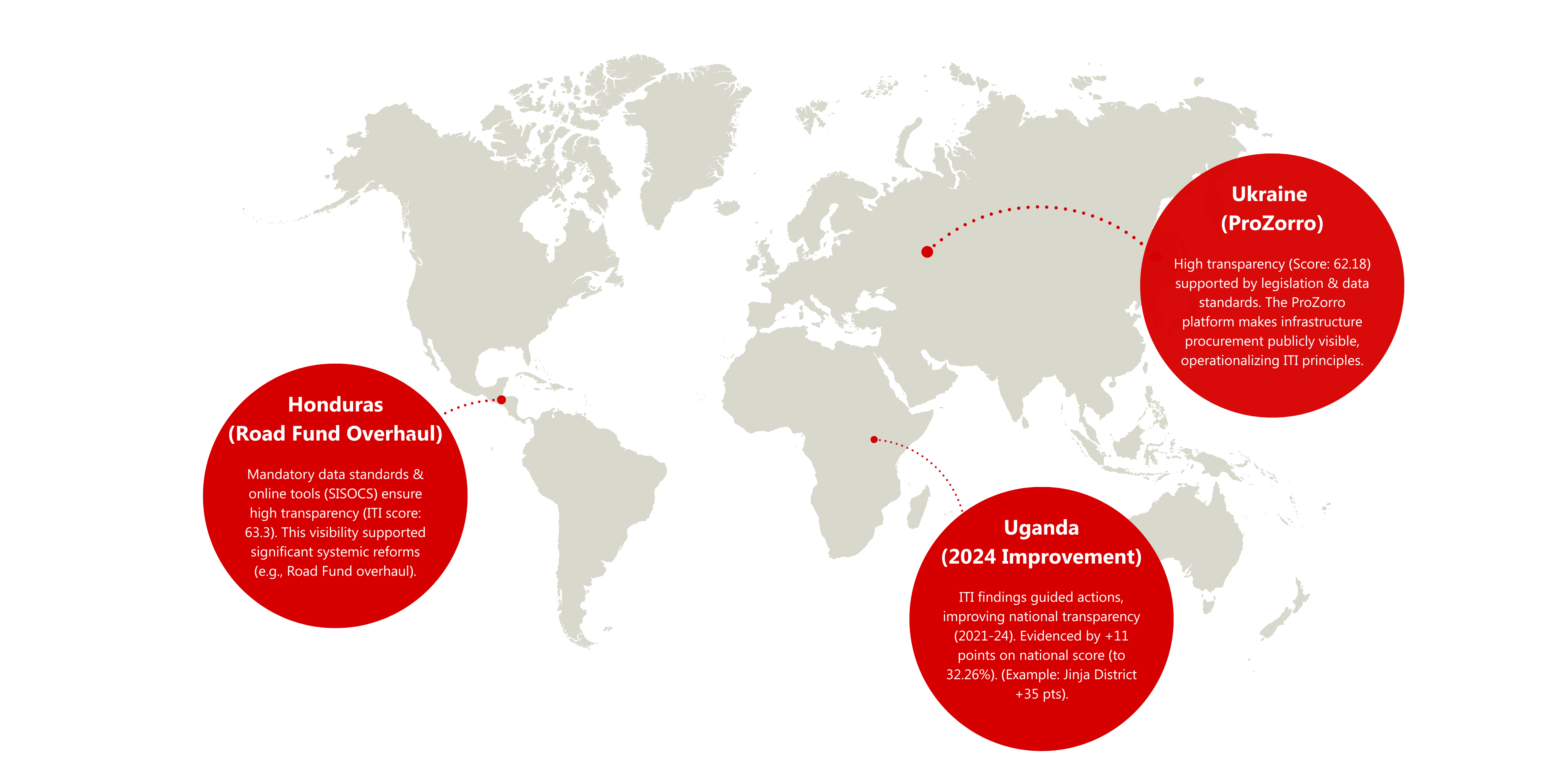
The ITI’s practical application has yielded demonstrable results across diverse contexts in CoST’s membership:The tool can also be by countries and regions outside of CoST membership.
The Professional Benefits of ITI Adoption
The ITI offers a compelling value proposition for a range of stakeholders within the infrastructure sector:
- Government Institutions: The ITI is a diagnostic tool for identifying inefficiencies, strengthening project management practices, and fostering public trust through demonstrable commitment to transparency, accountability and participation. The case of Uganda illustrates the direct benefits of utilizing ITI data to target areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
- Private Sector: Ihe ITI promotes a more transparent and equitable bidding environment. As evidenced in Thailand, enhanced transparency in procurement processes reduces corruption risks and fosters fair competition, creating a more predictable and stable business landscape.
- Civil Society and Media: The ITI empowers civil society organizations and media with objective data to hold decision-makers accountable and advocate for improved governance. In Uganda, journalists have been trained to effectively utilise ITI data to enhance public awareness and exert pressure for greater accountability.
- Citizens: Ultimately, the public benefits most directly from the enhanced transparency, participation and accountability fostered by the ITI. Improved infrastructure management translates to more effective public services, which can enhance quality of living standards and supports optimised use of taxpayer funds.
Call to Action: Embracing the ITI for Infrastructure Excellence
The ITI is more than an assessment tool; it is a strategic framework for driving continuous improvement in infrastructure transparency and performance.
To leverage the benefits of the ITI:
- Consult the ITI Manual: For a more comprehensive understanding of the methodology and implementation guidelines, the Infrastructure Transparency Index Manual is an invaluable resource.
- Engage with the ITI website: Explore the website to access further information, resources and country comparisons on the ITI and CoST’s global initiatives.
- Promote ITI Adoption: Advocate for the adoption and implementation of the ITI within your respective spheres of influence, whether in policy-making, private sector, civil society, or media.
 Cengkuru Michael
Cengkuru Michael
Cengkuru Michael is a passionate IT and data specialist who, through his work with CoST, the Infrastructure Transparency Initiative, significantly promotes transparency and accountability in public infrastructure worldwide. As a key member of the CoST International Secretariat based in Kampala, Uganda, Michael leverages his data analysis, IT, and communication expertise to advance CoST’s mission across its network.