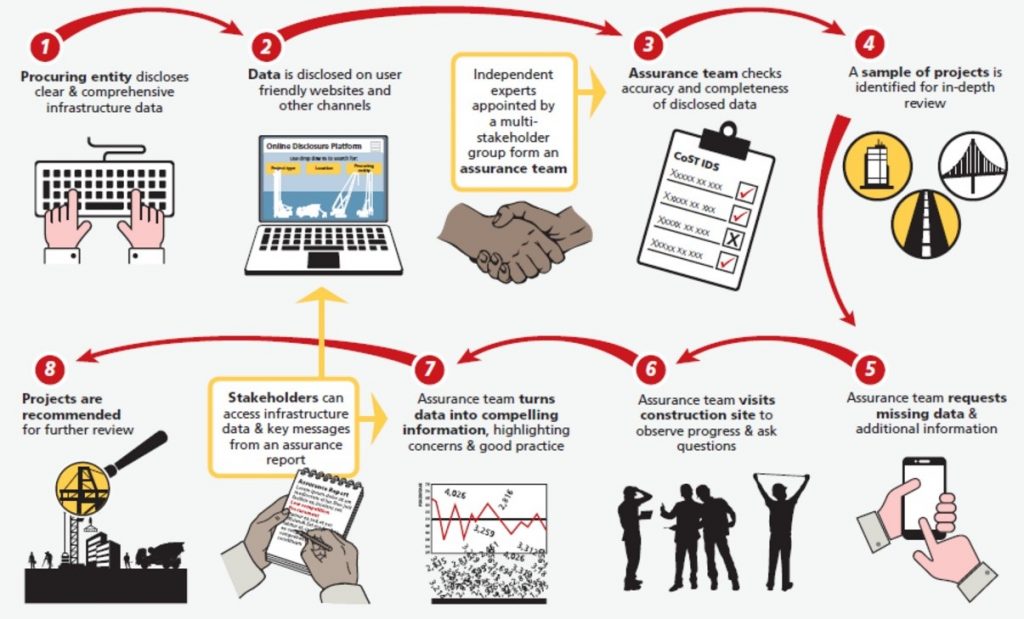
Our independent review (assurance) process helps stakeholders to understand the data published on specific infrastructure projects in the process of publishing data. The process is carried out by an independent assurance team appointed by our members who highlight the accuracy and completeness of data. They turn data into compelling information so that key issues are put into the public domain and are easily understood.
The process of independently reviewing data:
- Monitors compliance during infrastructure projects in accordance with any relevant legal provisions on publishing data or with the CoST International Data Standard
- Highlights issues of concern
- Carries out a more detailed review of a sample of projects or relevant projects to an independent authority.
In the initial stages of membership, only a small number of projects are selected for inclusion in the assurance process. If the data highlights key issues or if there are gaps in the data, more independent reviews are undertaken on the relevant procuring entities.
After a longer period of membership, members move towards gathering more extensive data and they begin to look at aggregating data, including by region, project type and/or across a sector.

Summarising the findings: assurance reports
The review process culminates in the production of an assurance report which focus on:
- The accuracy and completeness of published information
- Common performance issues across projects
- Issues of concern on specific projects
- An evaluation of the issues and common themes
- Recommendations
Like the review process, the report may focus on infrastructure projects focusing on healthcare, housing, education, climate resilience, water and sanitation and more. The report uses language and a format that can be easily understood so that social accountability can happen in the best way possible and decision-makers are held to account.
After the assurance report has been produced, social accountability happens with civil society and the media helping to promote report findings and recommendations in the public domain. Members’ findings regularly achieve media coverage, and endorsements from civil society.
Useful links
Our Assurance Manual is a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to producing independent review reports, also available as Manual De Aseguramiento (Spanish).
The manual is accompanied by the Assurance Guidance Note, which provides an overview of independently reviewing data and key steps to implementing a process. Also available as Nota de Orientación: Aseguramiento (Spanish).
CoST member assurance reports can be found on our member pages.
Our Step by step template (also below) provides a useful overview.